
5G deployment of optical module applications
5th Generation Mobile Communication Technology abbreviated as 5G,it is a new generation of broadband mobile communication technology with characteristics of high speed, low latency, and large connectivity. 5G communication infrastructure is the network infrastructure for achieving human-machine and object interconnection.
The International Telecommunication Union (ITU) defines three major application scenarios for 5G, namely Enhanced Mobile Broadband (eMBB), Ultra Reliable Low Latency Communication (uRLLC), and massive Machine Type of Communication (mMTC). eMBB is mainly aimed at the explosive growth of mobile Internet traffic, providing more extreme application experience for mobile Internet users; uRLLC is mainly aimed at vertical industry applications such as industrial control, telemedicine, and autonomous driving, which have extremely high requirements for time delay and reliability; mMTC is mainly aimed at applications such as smart cities, smart homes, and environmental monitoring that target sensing and data collection.
With the continuous progress of science and technology, 5G network has become one of the hot topics in today's communication field. 5G technology will not only provide us with faster data transfer speeds, but also support more connections between devices, thus creating more possibilities for future smart cities, autonomous vehicles and the Internet of Things. However, behind the 5G network, there are many key technologies and equipment support, one of which is the optical module.
The optical module is the core component of optical communication, which mainly completes the photoelectric conversion, the sending end converts the electrical signal into the optical signal, and the receiving end converts the optical signal into the electrical signal. As the core device, optical module is widely used in communication equipment and is the key to realizing high bandwidth, low delay and wide connection of 5G.
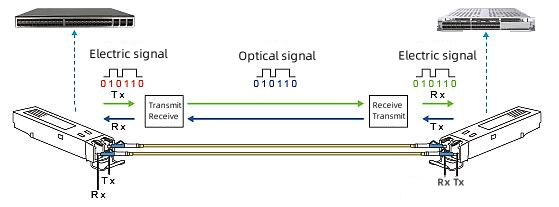
Base station connection: 5G base stations are usually located in high-rise buildings, telecommunications towers, and other places, and they need to quickly and reliably transmit data to user devices. Optical modules can provide high-speed and low latency data transmission, ensuring that users can access high-quality communication services.

Data center connectivity: Data centers can store and process large amounts of data to meet user needs. Optical modules are used to connect between different data centers, as well as between data centers and base stations, ensuring that data can be transferred quickly and efficiently.
The overall structure of communication networks for telecommunications operators usually includes backbone networks and metropolitan area networks. The backbone network is the operator's core network, and the metropolitan area network can be divided into core layer, aggregation layer, and access layer. Telecom operators build a large number of communication base stations in the access layer, covering network signals to various areas, allowing users to access the network. At the same time, communication base stations transmit user data back to the backbone network of telecommunications operators through the metropolitan aggregation layer and core layer network.
In order to meet the requirements of high bandwidth, low latency, and wide coverage, the 5G wireless access network (RAN) architecture has evolved from a two-level structure of 4G baseband processing unit (BBU) and radio frequency pull-out unit (RRU) to a three-level structure of centralized unit (CU), distributed unit (DU), and active antenna unit (AAU). The 5G base station equipment integrates the original RRU equipment and antenna equipment of 4G into a new AAU equipment, while splitting the original BBU equipment of 4G into DU and CU equipment. In the 5G carrier network, the AAU and DU devices form a forward transmission, the DU and CU devices form an intermediate transmission, and the CU and backbone network form a backhaul.
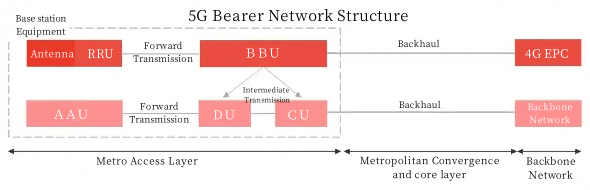
The three-level architecture used by 5G base stations adds a layer of optical transmission link compared with the second-level architecture of 4G base stations, and the number of optical ports increases, so the demand for optical modules also increases.
1. Metro Access Layer:
The metro access layer, the optical module is used to connect 5G base stations and transmission networks, supporting high-speed data transmission and low-latency communication. Common application scenarios include optical fiber direct connection and passive WDM.
2. Metropolitan Convergence layer:
At the metropolitan convergence layer, optical modules are used to aggregate data traffic at multiple access layers to provide high-bandwidth and high-reliability data transmission. Need to support higher transmission rates and coverage, such as 100Gb/s, 200Gb/s, 400Gb/s, etc.
3. Metropolitan core layer/Provincial Trunk Line:
In core layer and trunk line transmission, optical modules undertake larger data transmission tasks, requiring high speed, long-distance transmission and powerful signal modulation technology, such as DWDM optical modules.
1. Increase in transmission rate:
With the high-speed requirements of 5G networks, the transmission rates of optical modules need to reach levels of 25Gb/s, 50Gb/s, 100Gb/s or even higher to meet the needs of high-capacity data transmission.
2. Adapt to different application scenarios:
The optical module needs to play a role in different application scenarios, including indoor base stations, outdoor base stations, urban environments, etc., and environmental factors such as temperature range, dust prevention and waterproofing need to be considered.
3. Low cost and high efficiency:
The large-scale deployment of 5G networks results in a huge demand for optical modules, therefore low cost and high efficiency are key requirements. Through technological innovation and process optimization, the manufacturing cost of optical modules is reduced, and production efficiency and capacity are improved.
4. High reliability and industrial grade temperature range:
The optical modules in 5G bearer networks need to have high reliability and be able to operate stably in harsh industrial temperature ranges (-40 ℃ to+85 ℃) to adapt to different deployment environments and application scenarios.
5. Optical performance optimization:
The optical module needs to optimize its optical performance to ensure stable transmission and high-quality reception of optical signals, including improvements in optical loss, wavelength stability, modulation technology, and other aspects.

In this paper, the optical modules used in 5G forward, intermediate and backpass applications are systematically introduced. The optical modules used in 5G forward, intermediate and backpass applications provide end-users with the best choice of high speed, low delay, low power consumption and low cost. In 5G bearer networks, optical modules, as an important part of the infrastructure, undertake key data transmission and communication tasks. With the popularization and development of 5G networks, optical modules will continue to face higher performance requirements and application challenges, requiring continuous innovation and progress to meet the needs of future communication networks.
Along with the rapid development of 5G networks, optical module technology is also continuously advancing. I believe that future optical modules will be smaller, more efficient, and able to support higher data transmission speeds. It can meet the growing demand for 5G networks while reducing energy consumption and minimizing the impact of communication networks on the environment. As a professional optical module supplier, the company will promote further innovation in optical module technology and work together to provide strong support for the success and sustainable development of 5G networks.
