Solution
Date Center
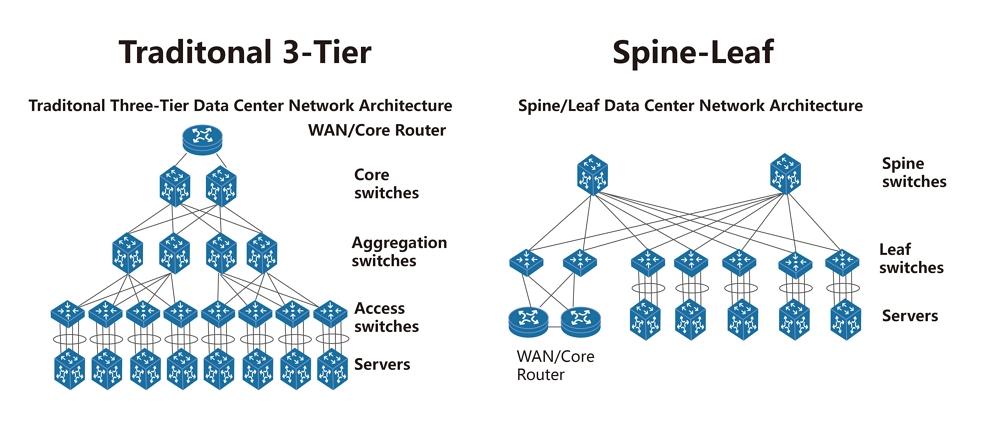
The basic architecture of a data center is to connect servers in a cabinet to low-level switches, and low-level switches to upper-layer switches. Early data centers adopted the traditional three-layer architecture of access-Aggregation-core, modeled after the telecommunications network with access-metro - backbone structure. This three-layer network structure is very suitable for the transmission between servers and external devices (north-south), and information is transmitted from outside the data center to the center.
As the demand for cloud computing and big data leads to an increase in data flow between servers (east-west), the market has begun to appear a two-tier leaf ridge architecture where the convergence layer and the core layer are fused. In this topology, the network is flattened from three layers to two layers, and all blade switches are connected to each ridge switch, so that data transmission between any server and another server only needs to go through one blade switch and one ridge switch, reducing the need for devices to find or wait for connections, reducing latency and reducing bottlenecks. It greatly improves the efficiency of data transmission and satisfies the high performance computing cluster application.
SOLUTION
Chengdu Sandao Technology Co., LTD.
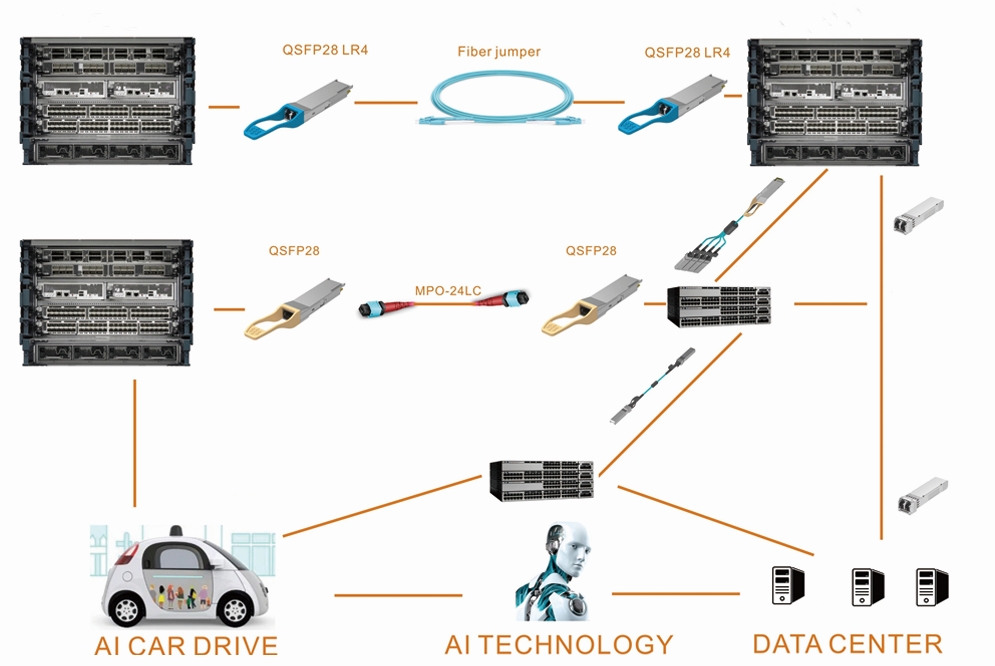
Typical scenarios
Features
Features of data center optical module requirements
