Performance evaluation of cable Jacket materials
As an important power and signal transmission tool, the cable is more and more widely used in various extreme environments. In various applications, cable sheath materials play an important role in protecting internal components of cables from environmental factors such as moisture, heat, and mechanical stress.
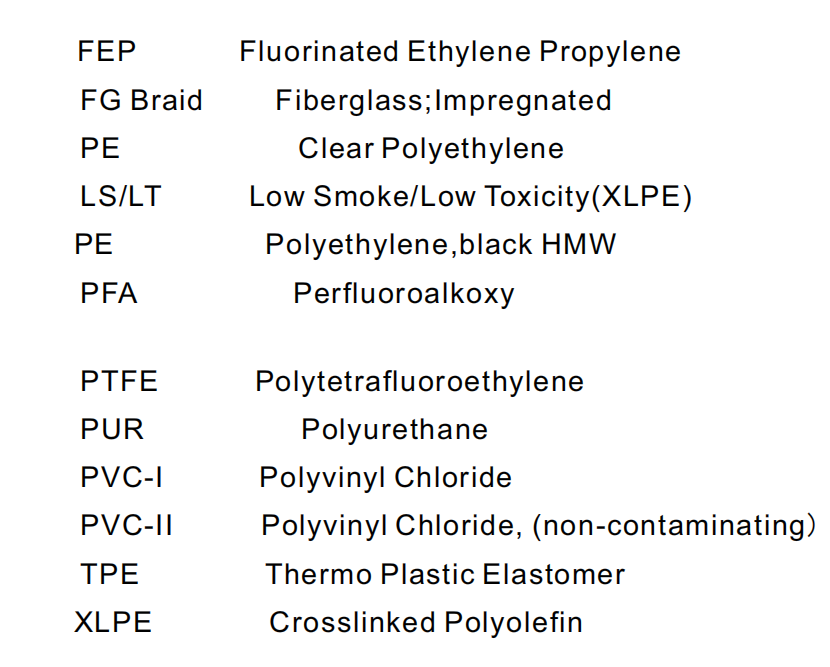
In this paper, eight commonly used cable sheathing materials - crosslinked polyethylene (XLPE), polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), fluorinated ethylene propylene (FEP), perfluoroalkoxy resin (PFA), polyurethane (PUR), polyethylene (PE), thermoplastic elastomer (TPE) and polyvinyl chloride (PVC) are taken as examples. They each have different performance characteristics, the purpose is to comprehensively evaluate the performance of these materials through practical testing and data analysis, and provide practical guidance for the design and application of cable jacket.
Jacket Materials:
Material performance research and practical testing
1. Temperature resistance test
We conducted temperature resistance tests on eight materials, including thermal aging and low-temperature impact tests.
Data analysis:
|
Material |
Temperature range of thermal aging(℃) |
Low temperature impact temperature(℃) |
XLPE |
-40 ~ 90 |
-60 |
PTFE |
-200 ~ 260 |
-200 |
FEP |
-80 ~ 200 |
-100 |
PFA |
-200 ~ 250 |
-150 |
PUR |
-40 ~ 80 |
-40 |
PE |
-60 ~ 80 |
-60 |
TPE |
-60 ~ 100 |
-40 |
PVC |
-10 ~ 80 |
-10 |
As can be seen from the data, PTFE and PFA have the widest temperature range and are particularly suitable for high and low temperature environments.

2. Water resistance test
We tested the material for water resistance, including soaking tests and water vapor transmittance tests.
Data analysis:
Material |
Water absorption rate(%) |
Water vapor transmittance (g/m²·24h) |
XLPE |
0.2 |
0.1 |
PTFE |
0.1 |
0.05 |
FEP |
0.1 |
0.08 |
PFA |
0.1 |
0.06 |
PUR |
0.3 |
0.15 |
PE |
0.4 |
0.2 |
TPE |
0.5 |
0.25 |
PVC |
0.8 |
0.3 |
From the data, it can be seen that PTFE, FEP, and PFA have lower water absorption and excellent water vapor barrier performance, demonstrating good water resistance.

3. Mold resistance test
We conducted long-term mold culture experiments to observe and record the growth of mold on the surface of each material.
Data analysis:
|
Material |
Mold growth situation |
XLPE |
Slight growth |
PTFE |
No growth |
FEP |
No growth |
PFA |
No growth |
PUR |
Slight growth |
PE |
Slight growth |
TPE |
Moderate growth |
PVC |
Significant growth |
From the data, it can be seen that PTFE, FEP, and PFA have excellent anti mold performance in humid environments.

4. Electrical performance test
The electrical properties of the material, such as insulation resistance and dielectric strength, were tested.
Data analysis:
Material |
Insulation resistance (Ω·m) |
Dielectric strength(kV/mm) |
XLPE |
10^14 |
30 |
PTFE |
10^18 |
60 |
FEP |
10^16 |
40 |
|
PFA |
10^17 |
50 |
PUR |
10^12 |
25 |
PE |
10^11 |
20 |
TPE |
10^13 |
35 |
PVC |
10^10 |
15 |
From the data, it can be seen that PTFE has the highest insulation resistance and dielectric strength, demonstrating excellent electrical performance. However, the electrical performance of PVC is relatively poor.

5. Mechanical property test
The mechanical properties such as tensile strength and elongation at break were tested.
Data analysis:
Material |
Tensile strength (MPa) |
Elongation at break(%) |
XLPE |
15-30 |
300-500 |
PTFE |
10-25 |
100-300 |
FEP |
15-25 |
200-400 |
PFA |
20-35 |
200-450 |
PUR |
20-40 |
400-600 |
PE |
10-20 |
300-500 |
TPE |
10-30 |
300-600 |
PVC |
25-45 |
100-200 |
Cables are often subjected to bending, twisting, and other forms of mechanical stress during installation and operation. Evaluating the tensile strength, flexibility, and abrasion resistance of jacket materials is essential in determining their ability to withstand such stresses without compromising the integrity of the cable.It can be seen from the data that PUR and TPE perform better in terms of tensile strength and elongation at break and have good mechanical properties, while PVC has relatively poor mechanical properties.

Based on the above data analysis, it is recommended that you choose the appropriate cable jacket material according to the specific application scenarios and requirements:
Temperature resistance: PTFE and PFA have the widest temperature range and are especially suitable for high and low temperature environments. These two materials are ideal for applications that require extreme temperatures.
Water resistance: PTFE, FEP and PFA have low water absorption and excellent water vapor barrier properties, showing good water resistance. These materials should be considered for cables used in wet or underwater environments.
Mold resistance: PTFE, FEP and PFA have excellent mold resistance in humid environments. These materials are preferred for cables that require long-term use in humid or mildew prone environments.
Electrical properties: PTFE has the highest insulation resistance and dielectric strength, showing excellent electrical properties. For applications that require high electrical performance, such as high-voltage cables or signal transmission cables, PTFE is the ideal choice.
Mechanical properties: PUR and TPE perform better in tensile strength and elongation at break, and have good mechanical properties. For cables that need to withstand greater mechanical stress or deformation, these two materials can be considered.
Overall, the performance evaluation of cable sheath materials includes a comprehensive evaluation of their resistance to environmental factors, electrical performance, mechanical strength, etc. Through comprehensive evaluation, manufacturers and users can make wise decisions to choose the cable sheath material that best suits their specific application requirements, ultimately improving the overall reliability and service life of the cable system.
The company provides solid theoretical support for promoting the comprehensive performance improvement and sustainable development of cable outer sheath materials. At the same time, with the continuous development of new material technology and the increasing application demand, we will look forward to more high-performance cable outer sheath materials with you, injecting new vitality into the progress of the cable industry.